Biomass is, “solid or liquid plant or animal origin, which are biodegradable, derived from products, waste and residues from agriculture and forestry, and related industries, as well as parts of other wastes that are biodegradable”.20 Biomass is a considerable alternative to fossil fuels in that it is carbon neutral meaning that any CO2 the biomass releases when burned is CO2 that the biomass had already captured.20 When biomass is burned, it lets off a steam that can heat developments, create electricity, or produce biofuel. 21
Click the image below for the 101 on biomass energy.
- Pros: The creation of biofuels reduces the amount of wastes in landfills20, biomass energy can be easily stored (unlike wind and solar energy), the sources are inexhaustible while still producing heat and electricity, biomass can be produced locally and therefore lessen any reliance on fossil fuels.22
- Cons: Greenhouse Gases are still emitted into the atmosphere during biomass production, extraction of biomass is expensive, it requires a large surface area for storage of biomass, it also requires a large amount of water22 and the success of biomass as energy production could lead to deforestation and land degradation that exotic and endangered species need for survival.
- Malaysia for example is a huge producer of palm oil which is a common source in food, biofuels and cosmetics.23 According to Wicke et al, Malaysia and most of Indonesia is projected to only have enough land to meet demands for palm oil until 2020, severe land degradation is expected there-after. In hand, being so reliant on biomass as a renewable energy source will also begin to dwindle.23
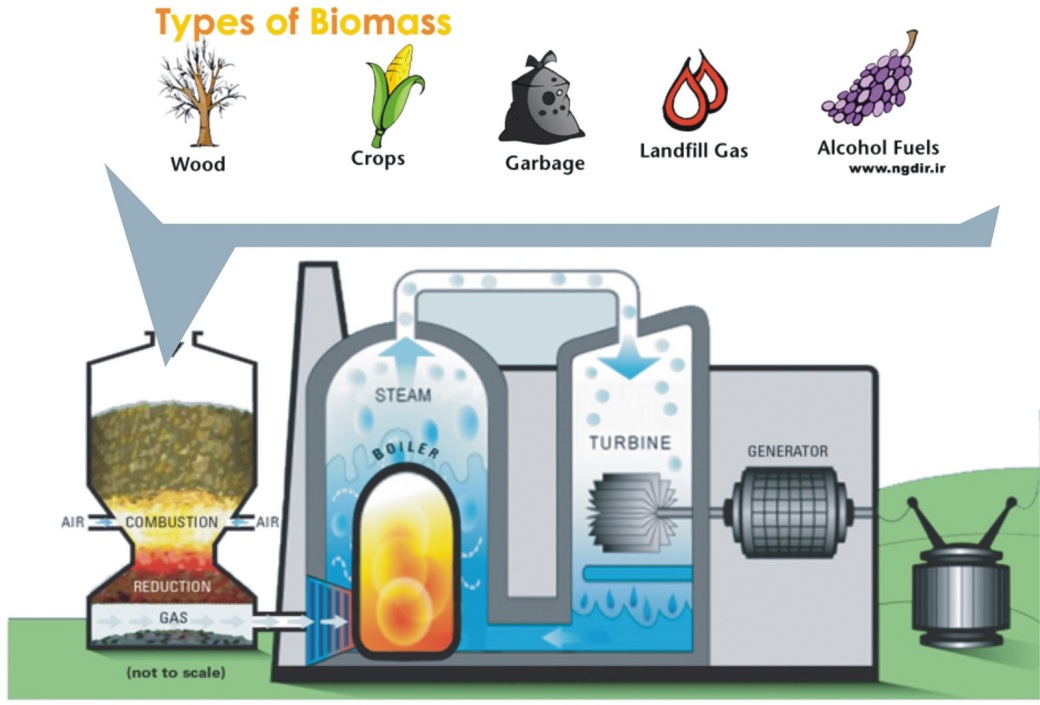
Image 9
