Wind energy is produced through wind turbines on both large and small scales. From windmills to wind farms, the energy from wind is quantitatively substantial and a pollution-free source of power.31 Though, like all great things, it has some drawbacks.
Click the image below for the 101 on wind energy.
- Pros: Wind energy does not contribute to the acceleration of global warming, it reduces the need for fuels that produce greenhouse gas emissions, it is an infinite source of energy both on the ocean side and inland, and wind energy is a moderately affordable renewable energy compared to most others, it also provides price stability for consumers.31
- Cons: Wind energy can have large start up costs, especially when developing wind farms that require ample amounts of already expensive materials, the ability to store the produced energy is inefficient, and the success of wind energy requires a suitable site. Wind energy also has a history of impacting wildlife’s habitats, including birds and marine species, along with being an eyesore and a noise polluter to the local populations nearby.31

Image 17
Wind energy is rapidly growing and readily advancing with new technologies that address the challenges with wind variability. The most efficient mitigation in dealing with wind variability thus far is wind collection over large balancing areas. In short, sites with consistent soft breezes will result in the most effective use of wind turbines for energy. Wind forecasting is another mitigation that will ensure maximum collection from day to day.32
Wind energy can be built on farms, ranches and coastlines that, in hand, benefit the economy in rural areas and though impacts are present, they are minimal. In fact, comparing to other green technologies, wind energy has the smallest carbon footprint (see image below).
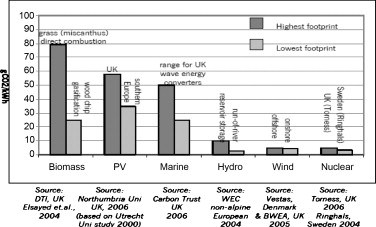
Image 18